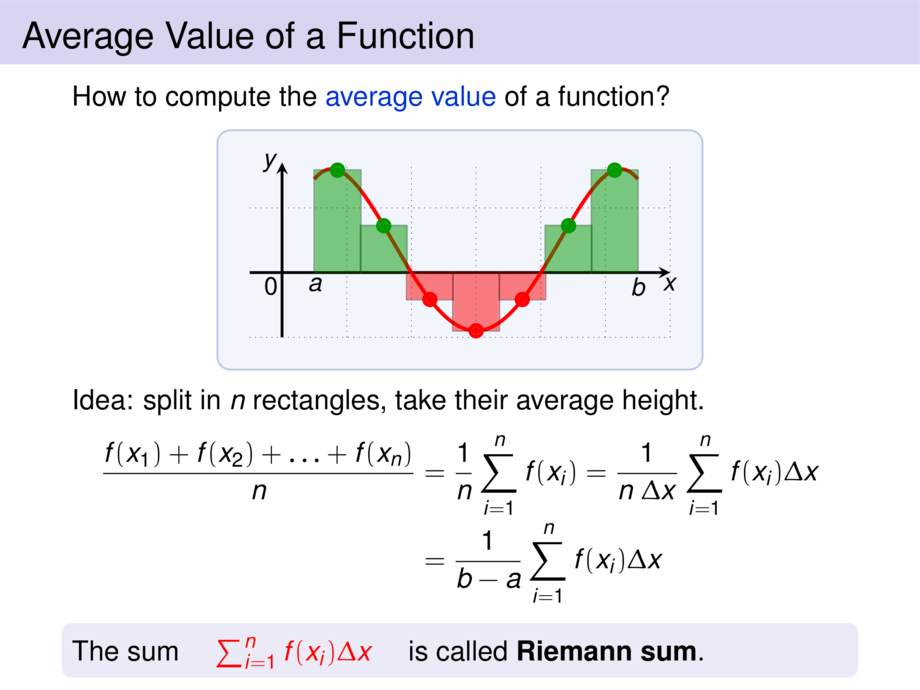
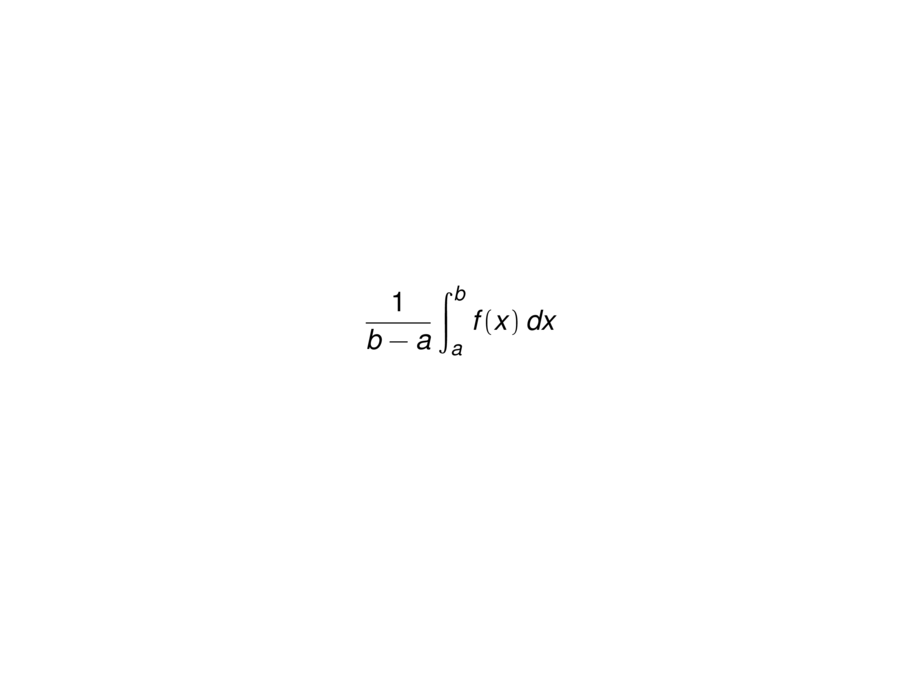

































































































19/50
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{Average Value of a Function}
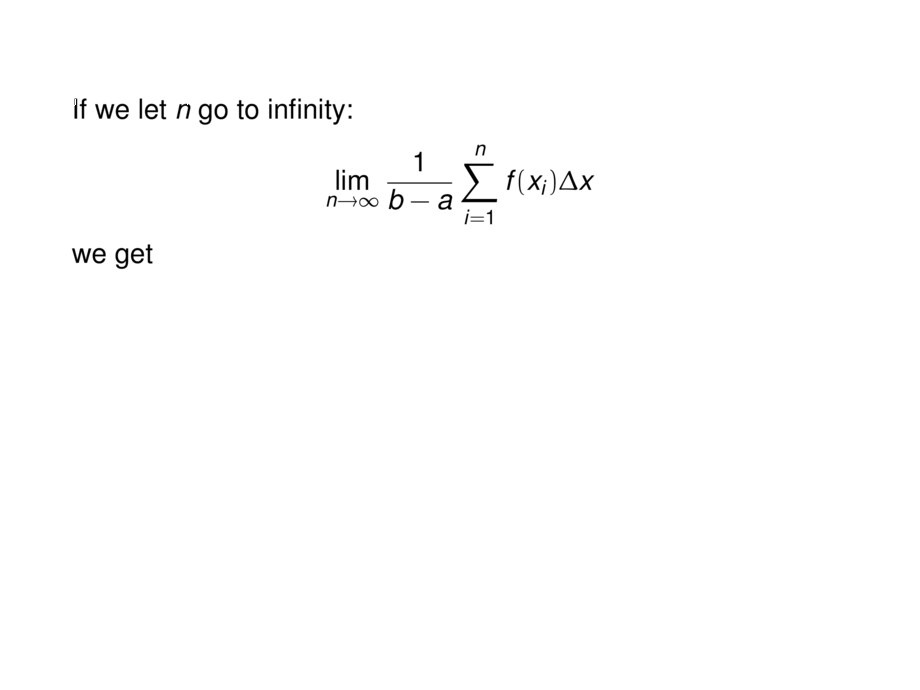
If we let $n$ go to infinity:
\begin{talign}
\lim_{n \to \infty} \frac{1}{b-a}\sum_{i = 1}^n f(x_i)\Delta x
\end{talign}
we get\pause
\begin{talign}
\frac{1}{b-a} \int_a^b f(x) \, dx
\end{talign}
\pause
As a consequence, we have
\begin{block}{}
The average value $f_{\text{avg}}$of a function $f$ on an interval $[a,b]$ is:
\begin{talign}
f_{\text{avg}} = \frac{1}{b-a} \int_a^b f(x) \, dx
\end{talign}
Thus the average value of the function is the integral over the interval divided by the width of the interval.
\end{block}
\end{frame}

