


































































































53/81
\begin{frame}
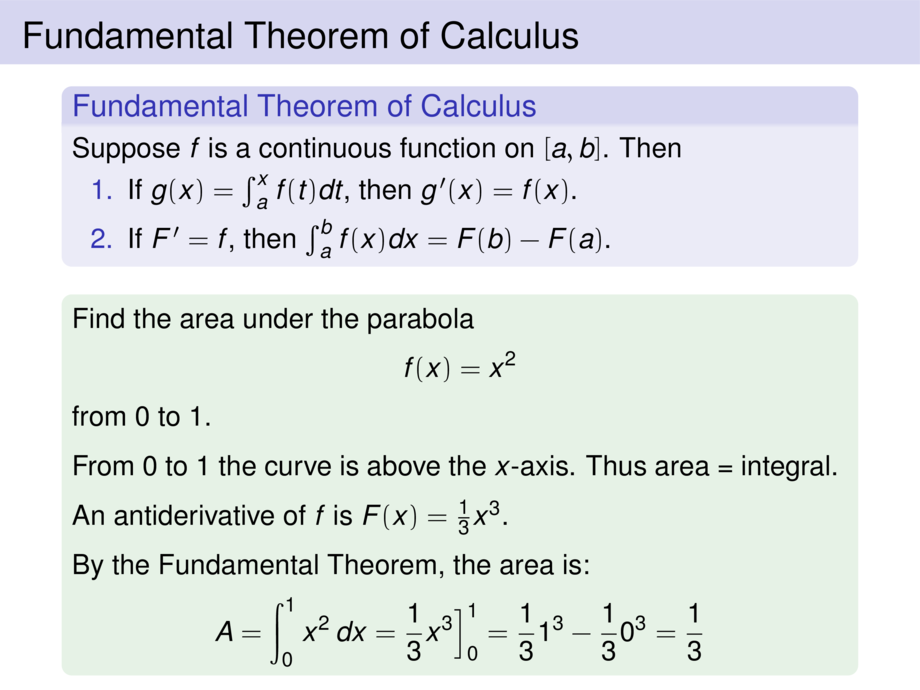
\frametitle{Fundamental Theorem of Calculus}
\fundamental
\medskip
\begin{exampleblock}{}
Find the area under the parabola
\begin{talign}
f(x) = x^2
\end{talign}
from $0$ to $1$.
\pause\medskip
From $0$ to $1$ the curve is above the $x$-axis. \pause Thus area = integral.
\pause\medskip
An antiderivative of $f$ is $F(x) = \pause \frac{1}{3}x^3$.
\pause\medskip
By the Fundamental Theorem, the area is:
\begin{talign}
A = \int_0^1 x^2 \, dx= \mpause[1]{\frac{1}{3}x^3 \Big]_0^1} \mpause{= \frac{1}{3}1^3 - \frac{1}{3}0^3} \mpause{= \frac{1}{3}}
\end{talign}
\end{exampleblock}
\vspace{10cm}
\end{frame}

