


































































































69/111
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{The Definite Integral}
\begin{exampleblock}{}
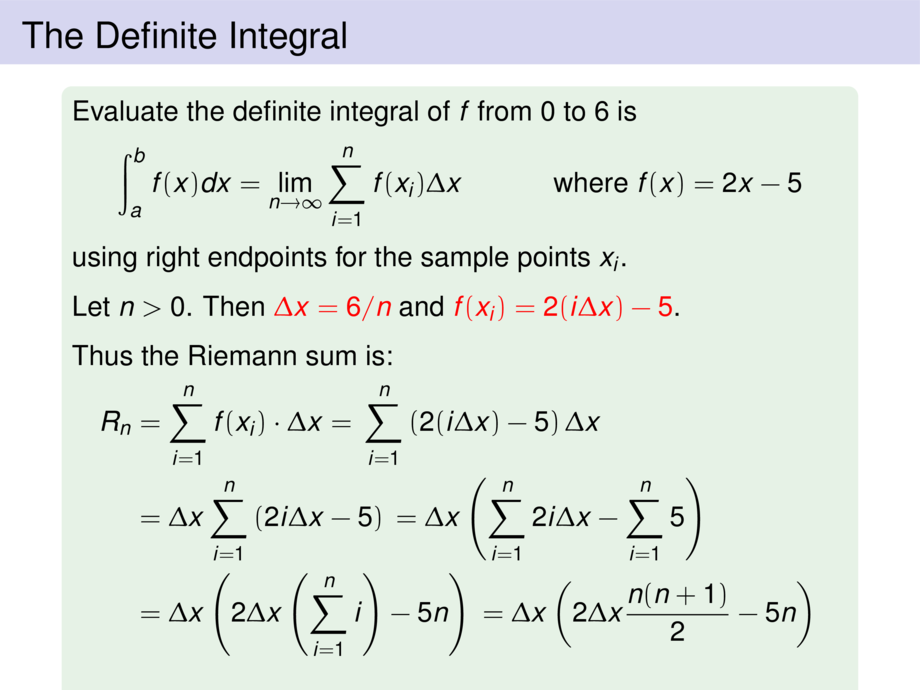
Evaluate the definite integral of $f$ from $0$ to $6$ is
\begin{talign}
\int_{a}^{b} f(x)dx = \lim_{n\to \infty} \sum_{i = 1}^n f(x_i) \Delta x &&&&\text{where $f(x) = 2x-5$}
\end{talign}
using right endpoints for the sample points $x_i$.
\pause\medskip
Let $n > 0$. Then \mpause[10]{\alert{$\Delta x = 6/n$} and \alert{$f(x_i) = 2(i\Delta x) - 5$}.}
\only<-11>{
\begin{itemize}
\pause
\item $\Delta x = \pause (6-0) / n \pause = 6/n$
\pause
\item the $i$-th interval is \pause $[0 + (i-1)\Delta x,\; 0+ i\Delta x]$
\pause
\item the right endpoints are $x_i = \pause i\Delta x$
\pause
\item the values at $x_i$'s are $f(x_i) = \pause 2(i\Delta x) - 5$
\end{itemize}
}
\pause[13]\medskip
Thus the Riemann sum is:
\only<-18>{
\begin{talign}
R_n
&= \sum_{i=1}^n f(x_i)\cdot \Delta x
= \mpause[1]{\sum_{i=1}^n \left(2(i\Delta x) - 5\right)\Delta x} \\
&\mpause{= \Delta x \sum_{i=1}^n \left(2i\Delta x - 5\right)}
\mpause{= \Delta x \left( \sum_{i=1}^n 2i\Delta x - \sum_{i=1}^n 5 \right)} \\
&\mpause{= \Delta x \left( 2\Delta x \left(\sum_{i=1}^n i\right) - 5n \right)}
\mpause{= \Delta x \left( 2\Delta x \frac{n(n+1)}{2} - 5n \right)}
\end{talign}
}
\pause[19]
\begin{talign}
R_n
&= \Delta x \left( 2\Delta x \frac{n(n+1)}{2} - 5n \right)
\mpause[1]{= \Delta x \left( \Delta x n(n+1) - 5n \right)} \\
&\mpause{= \frac{6}{n} \left( \frac{6}{n} n(n+1) - 5n \right)}
\mpause{= \frac{6}{n} \left( 6(n+1) - 5n \right)} \\
&\mpause{= \frac{6}{n} \left( n+1 \right)}
\mpause{= \frac{6n + 6}{n} } \\
\mpause{ \alert{\int_{a}^{b}}& \alert{f(x)dx} = \lim_{n\to \infty} R_n = }
\mpause{\lim_{n\to \infty} \frac{6n + 6}{n}}
\mpause{\alert{= 6}}
\end{talign}
\end{exampleblock}
\vspace{10cm}
\end{frame}

