


































































































36/111
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{The Definite Integral}
\begin{block}{}
If the limit
\begin{talign}
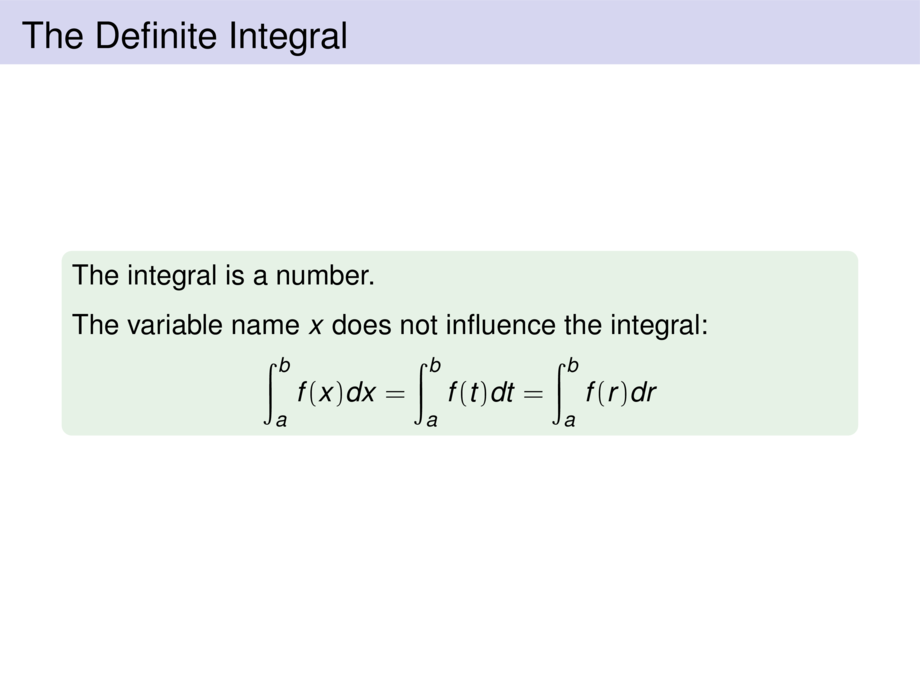
\int_{a}^{b} f(x)dx = \lim_{n\to \infty} \sum_{i = 1}^n f(x_i) \Delta x
\end{talign}
exists, then $f$ is called \emph{integrable} on $[a,b]$.
\end{block}
\pause\bigskip
Note every function is integrable.
\pause\bigskip
However, most of the functions we work with are:
\pause
\begin{block}{}
If
\begin{itemize}
\item $f$ is continuous on $[a,b]$, or
\item $f$ has only a finite number of jump discontinuities,
\end{itemize}
then $f$ is integrable on $[a,b]$,
that is, the $\int_{a}^{b} f(x)dx$ exist.
\end{block}
\vspace{10cm}
\end{frame}

