


































































































11/50
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{Newton's Method}
\begin{center}
\scalebox{.8}{
\begin{tikzpicture}[default,baseline=1cm]
\diagram{-.5}{4}{-.5}{4}{1}
\diagramannotatez
\begin{scope}[ultra thick]
\draw[cgreen,ultra thick] plot[smooth,domain=-0:3.3,samples=200] function{-.5 + (.5*x)**3};
\node[include=cgreen] (r) at (1.58,0) {};
\node[anchor=south east] at (r) {$r$};
\end{scope}
\mpause[1]{
\draw[gray] (3.2,-.2) -- node[at start,below,black] {$x_1$} node[include=cred,at end] {} (3.2,{-.5 + (.5*3.2)^3});
}
\mpause{
\tangent{4cm}{.5cm}{-.5 + (.5*\x)^3}{3.2}
}
\mpause{
\draw[gray] (2.28,-.2) -- node[at start,below,xshift=1mm,black] {$x_2$} (2.28,.2);
}
\end{tikzpicture}
}
\end{center}
\begin{exampleblock}{Idea of Newton's Method}
\begin{itemize}
\pause
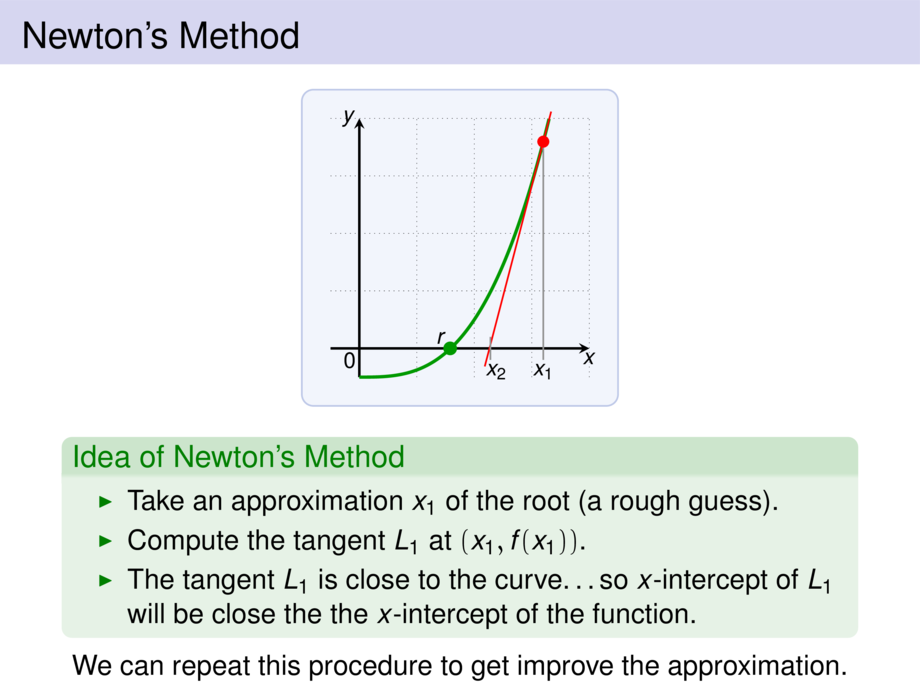
\item Take an approximation $x_1$ of the root (a rough guess).
\pause
\item Compute the tangent $L_1$ at $(x_1,f(x_1))$.
\pause
\item The tangent $L_1$ is close to the curve\ldots
so $x$-intercept of $L_1$ will be close the the $x$-intercept of the function.
\end{itemize}
\end{exampleblock}
\pause
We can repeat this procedure to get improve the approximation.
\vspace{10cm}
\end{frame}

