


































































































92/118
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{L'Hospital's Rule}
\begin{block}{}
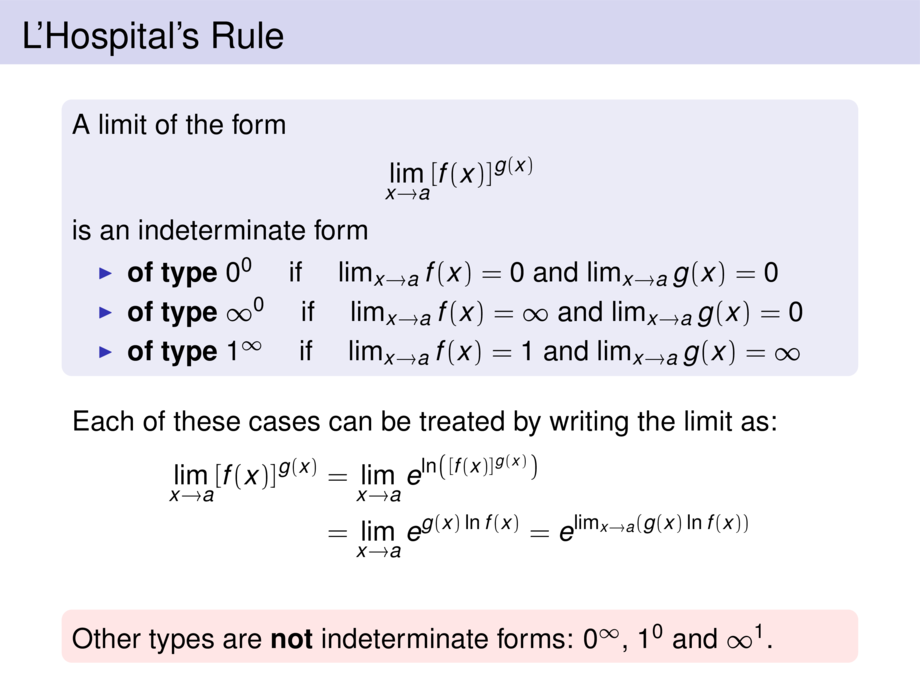
A limit of the form
\begin{talign}
\lim_{x \to a} [f(x)]^{g(x)}
\end{talign}
is an indeterminate form
\begin{itemize}
\item \emph{of type $0^0$} \quad if \quad $\lim_{x \to a} f(x) = 0$ and $\lim_{x \to a} g(x) = 0$
\item \emph{of type $\infty^0$} \quad if \quad $\lim_{x \to a} f(x) = \infty$ and $\lim_{x \to a} g(x) = 0$
\item \emph{of type $1^\infty$} \quad if \quad $\lim_{x \to a} f(x) = 1$ and $\lim_{x \to a} g(x) = \infty$
\end{itemize}
\end{block}
\pause\medskip
Each of these cases can be treated by writing the limit as:
\begin{talign}
\lim_{x \to a} [f(x)]^{g(x)}
&= \lim_{x \to a} e^{\ln \left( [f(x)]^{g(x)} \right)} \\
&\mpause[1]{= \lim_{x \to a} e^{g(x) \ln f(x)} }
\mpause[2]{= e^{\lim_{x \to a} \left( g(x) \ln f(x) \right)}}
\end{talign}
\pause\pause\pause
\begin{alertblock}{}
Other types are \emph{not} indeterminate forms: $0^\infty$, $1^0$ and $\infty^1$.
\end{alertblock}
\end{frame}

