


































































































90/154
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{One-Sided Limits: Example}
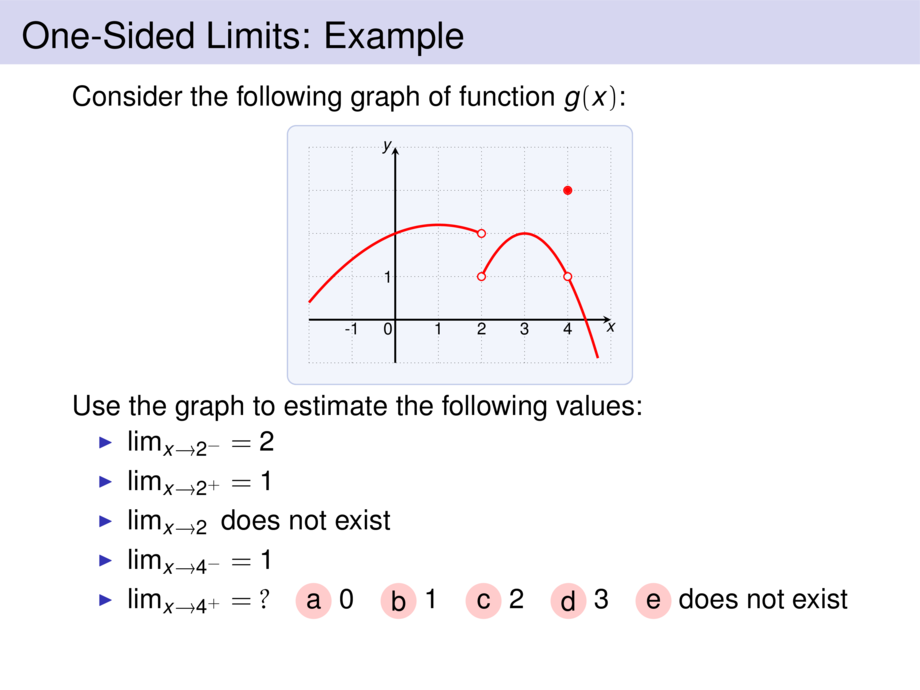
Consider the following graph of function $g(x)$:
\begin{center}
\scalebox{.6}{
\begin{tikzpicture}[default]
\diagram{-2}{5}{-1}{4}{1}
\diagramannotatez
\diagramannotatex{-1,1,2,3,4}
\diagramannotatey{1}
\draw[cred,ultra thick] plot[smooth,domain=-2:2,samples=20] function{2.2-.2*(x-1)**2};
\draw[cred,ultra thick] plot[smooth,domain=2:4.7,samples=20] function{2-(x-3)**2};
\node[exclude={cred}] at (2,2) {};
\node[exclude={cred}] at (2,1) {};
\node[exclude={cred}] at (4,1) {};
\node[include={cred}] at (4,3) {};
\end{tikzpicture}
}
\end{center}
\vspace{-1ex}
Use the graph to estimate the following values:
\begin{itemize}
\pause
\item $\lim_{x\to 2^-} = \alt<-2>{?}{2}$ \only<-2>{\choice{a} $0$ \choice{b} $1$ \choice{c} $2$ \choice{d} $3$ \choice{e} does not exist}
\pause\pause
\item $\lim_{x\to 2^+} = \alt<-4>{?}{1}$ \only<-4>{\choice{a} $0$ \choice{b} $1$ \choice{c} $2$ \choice{d} $3$ \choice{e} does not exist}
\pause\pause
\item $\lim_{x\to 2} \alt<-6>{= ?}{\text{ does not exist}}$ \only<-6>{\choice{a} $0$ \choice{b} $1$ \choice{c} $2$ \choice{d} $3$ \choice{e} does not exist}
\pause\pause
\item $\lim_{x\to 4^-} = \alt<-8>{?}{1}$ \only<-8>{\choice{a} $0$ \choice{b} $1$ \choice{c} $2$ \choice{d} $3$ \choice{e} does not exist}
\pause\pause
\item $\lim_{x\to 4^+} = \alt<-10>{?}{1}$ \only<-10>{\choice{a} $0$ \choice{b} $1$ \choice{c} $2$ \choice{d} $3$ \choice{e} does not exist}
\pause\pause
\item $\lim_{x\to 4} = \alt<-12>{?}{1}$ \only<-12>{\choice{a} $0$ \choice{b} $1$ \choice{c} $2$ \choice{d} $3$ \choice{e} does not exist}
\end{itemize}
\pause
\vspace{10cm}
\end{frame}

