
































































































17/101
\begin{frame}
\frametitle{Functions}
\begin{block}{}
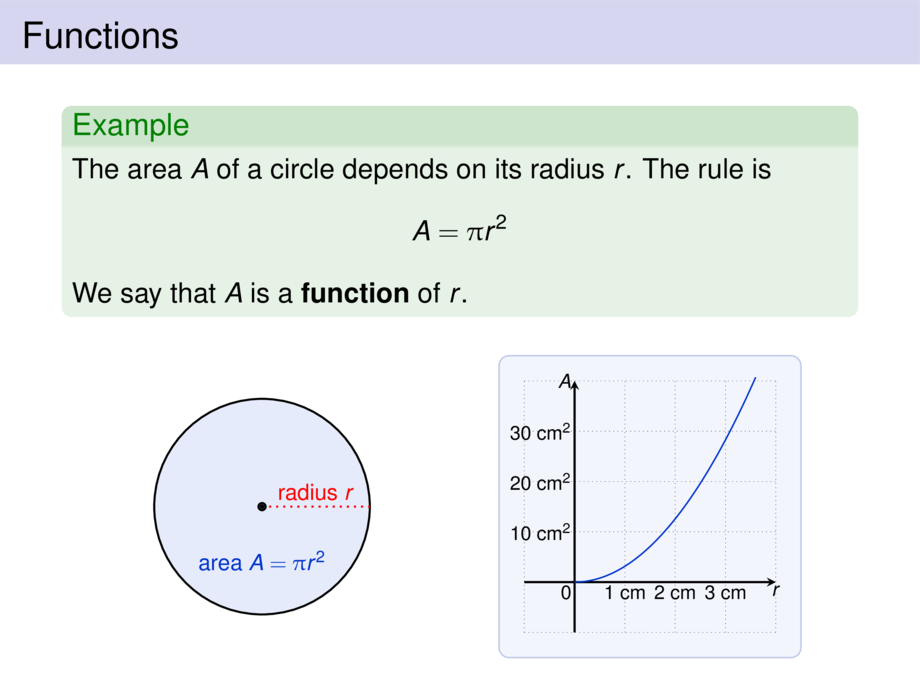
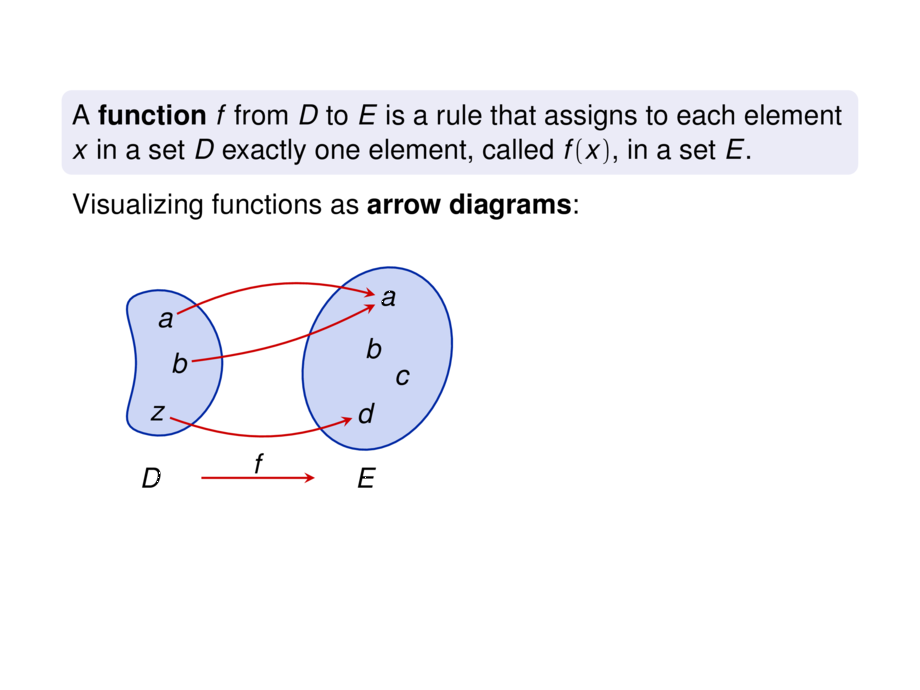
A \emph{function} $f$ from $D$ to $E$ is a rule that
assigns to each element $x$ in a set $D$
exactly one element, called $f(x)$, in a set $E$.
\end{block}
Visualizing functions as \emph{arrow diagrams}:
\begin{minipage}{.55\textwidth}
\begin{center}
\begin{tikzpicture}[default]
\draw [fill=cblue!20,draw=cdblue] (0cm,0cm) to[out=10,in=90] (1cm,-1cm) to[out=-90,in=-10] (0cm,-2cm) to[out=170,in=-90,looseness=1.5] (-.2cm,-1cm) to[out=90,in=190,looseness=1.5] (0,0);
\node (D) at (0,-2.6cm) {$D$};
\node (x) at (.2cm,-.4cm) {$a$};
\node (a) at (.4cm,-1cm) {$b$};
\node (z) at (.1cm,-1.7cm) {$z$};
\begin{scope}[xshift=35mm]
\draw [fill=cblue!20,draw=cdblue,rotate=-20] (0cm,-1cm) ellipse (1cm and 1.3cm);
\node (E) at (-.5,-2.6cm) {$E$};
\node (a') at (-.2cm,-.1cm) {$a$};
\node (c') at (-.4cm,-.8cm) {$b$};
\node (q') at (-.5cm,-1.7cm) {$d$};
\node (p') at (-0cm,-1.2cm) {$c$};
\end{scope}
\begin{scope}[cdred,->,>=stealth,thick]
\draw (x) to[bend left=20] (a');
\draw (a) to[bend left=-10] (a');
\draw (z) to[bend left=-20] (q');
\draw [shorten >= 5mm, shorten <= 5mm] (D) to node [above,black] {$f$} (E);
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{center}
\end{minipage}
\begin{minipage}{.44\textwidth}
\pause\pause\pause\pause
\begin{exampleblock}{This example}
\begin{itemize}
\pause
\item domain $D = \{\;a,b,z\;\}$
\pause
\item $E = \{\;a,b,c,d\;\}$
\pause
\item $f(a) = \pause a$
\pause
\item $f(b) = \pause a$
\pause
\item $f(z) = \pause d$
\pause
\item range $= \pause\{\;a,d\;\}$
\end{itemize}
\end{exampleblock}
\end{minipage}
\setcounter{beamerpauses}{1}
\pause
Terminology:
\begin{itemize}
\item $f(x)$ is the value of $f$ at $x$
\pause
\item \emph{domain} of $f$ is the set $D$
\pause
\item \emph{range} of $f$ is the set of all possible values $f(x)$ for $x$ in $D$
\end{itemize}
\end{frame}

